Comprehensive quality assurance is an imperative factor in serial production based on additive methods. In practice, however, lack of experience and expertise often cause failure in AM serial production. DIN SPEC 17071 provides guidance for users and manufacturers seeking to set up production lines more quickly.
When highly sensitive equipment is combined with the lack of technological maturity of some methods or insufficient experience with their application, deviations in the dimensions and strength values of AM products often result. Yet standardized and reproducible quality characteristics are imperative in high-volume production. This particularly applies to the production of safety components and regulated sectors, such as the industries MedTech, aerospace, transportation, and energy.
Achievement of high component quality requires complete specification of the entire production process and continuous quality assurance covering the preparation of data and processes as well as the manufacturing process itself and even extending to follow-up. This also takes in detailed quality characteristics plus the pertinent test methods, equipment, and environmental conditions for every individual process. Further critical factors are qualified personnel and end-to-end documentation.
Requirements definition and validation
DIN SPEC 17071 provides step-by-step guidance from process qualification to quality assurance and validation of requirements. In doing so, it focuses on the cross-industry state of the art in additive manufacturing and the applicable standards. By following this guidance, users can now establish production lines which include risk minimisation and quality assurance within only a few months – a process that sometimes took years in the past. DIN SPEC 17071 supports manufacturers in areas such as creating complete requirements specifications for suppliers and contract manufacturers, helping them to reduce the required number of supplier audits.
TÜV SÜD developed its certification scheme for additive manufacturing facilities based on DIN SPEC 17071 and best practice methods drawn directly from AM production. The certification scheme helps manufacturers to establish serial additive manufacturing. In addition, it provides manufacturers that successfully complete auditing with evidence to demonstrate their implementation of DIN SPEC 17071 and with criteria for ensuring reliable and assured product quality to their customers and business partners.
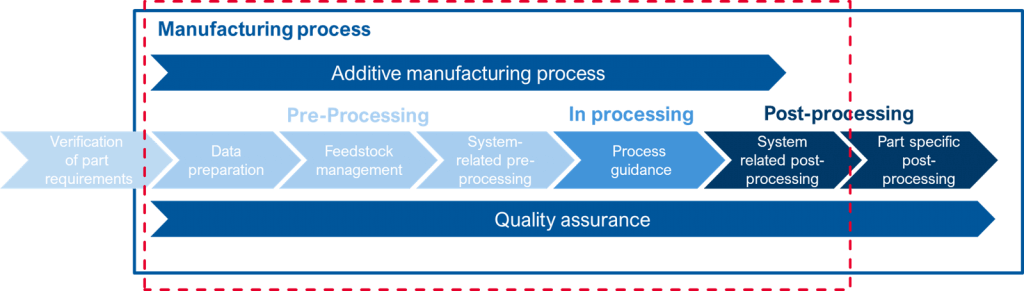
DIN SPEC 17071 provides step-by-step guidance from process qualification to quality assurance and validation of requirements. In doing so, it focuses on the cross-industry state of the art in additive manufacturing and the applicable standard.
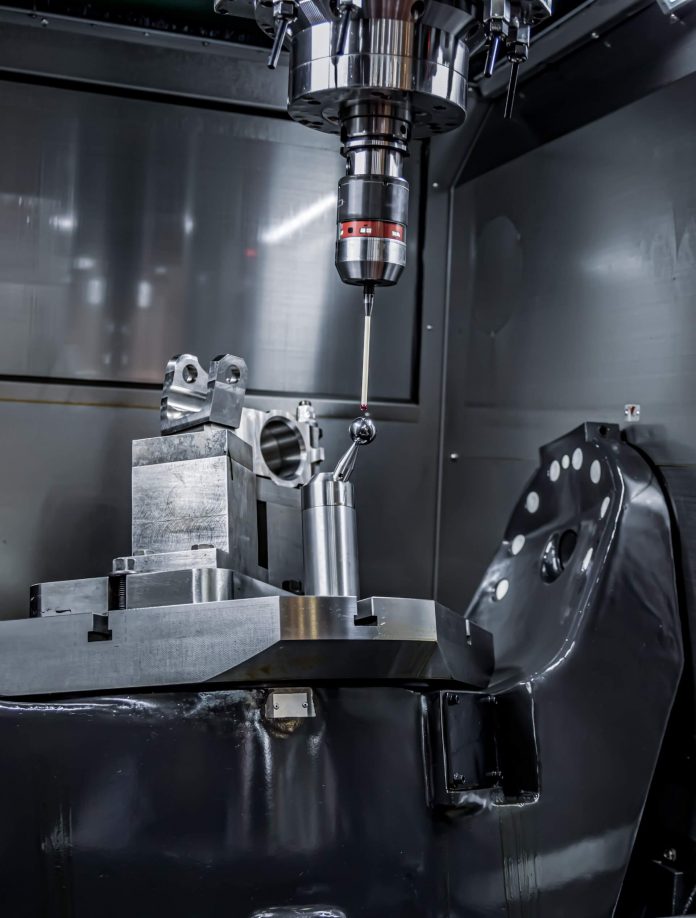
One case study for the establishment, assessment and certification of a production line concerns a German medium-sized enterprise that commissioned TÜV SÜD Product Service to assess its quality management in the field of additive manufacturing. The company produces plastic components for the automotive, mechanical engineering, and medtech industries. The external auditors assessed materials and machine handling, the definitions of quality criteria and order processing as well as the management of manufacturing processes and documentation. Further aspects concerned occupational health and safety and employee qualification.
The company uses the powder bed fusion (PBF) method, in which material in powder form is transformed into solid plastic by the application of focused heat. Depending on the feedstock and component design, this requires adjustment of various parameter settings including laser energy, exposure rate, and temperature. To ensure the component has the correct strength values later on, the powder solidification must be consistent in every production run. The raw material also plays a significant role in this respect. Its quality, handling, and storage are equally important for reproducible product quality in serial production.
DIN SPEC 17071 as the basis for ISO standards
So far there have been very few ISO and DIN standards addressing quality assurance in additive manufacturing. ISO 9001, for example, defines the general minimum requirements for QM systems. However, there are still many requirements and methods in additive manufacturing over which no final or fully developed consensus has been reached to date. ISO Committee TC 261 “Additive Manufacturing“ is currently working on many of these open issues. DIN SPEC 17071 is not a standard and is not integrated into existing EU Directives. However, it is a precursor of the forthcoming ISO/ASTM 52920-2 standard and is already helping pioneers in additive manufacturing to get their production lines ready for serial production and position themselves on the market.