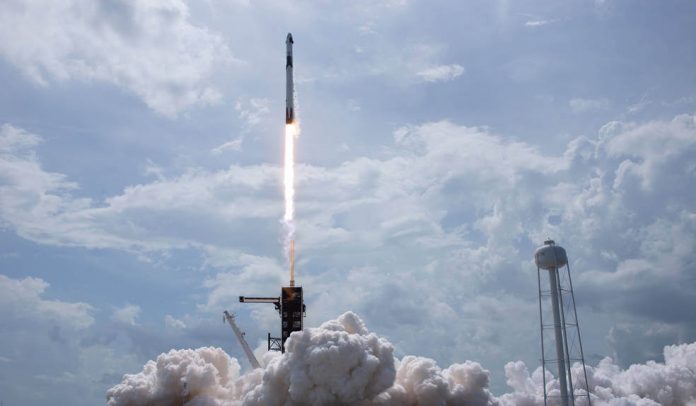
The Crew Dragon launched astronauts from US soil for the first time since the last Shuttle flight in 2011. But it’s a very different type of vehicle to Nasa’s retired spaceplane.
Elon Musk says human spaceflight had always been the fundamental goal for his pioneering company SpaceX.
The entrepreneur achieved that ambition on Saturday 30 May 2020, when the Crew Dragon spacecraft carried Nasa astronauts Doug Hurley and Bob Behnken into orbit for a rendezvous with the International Space Station (ISS).
But the company had to walk before it could run. Crew Dragon evolved from an earlier design, called Dragon 1, which launched 20 times on missions to deliver cargo to the ISS between May 2012 and March 2020.
In May 2014, Musk unveiled the seven-seat Crew Dragon concept during an event at SpaceX’s headquarters in Hawthorne, California.
Like Dragon 1, the crewed version is a capsule design, making it more similar to the Apollo command modules that carried astronauts to the Moon than the winged space shuttle concept, which was conceived to carry both a crew and a large payload.
From launch up until shortly before re-entry, the capsule is attached to a section called the trunk which has solar panels, heat-removal radiators and fins to provide stability during emergency aborts. Together, the capsule and trunk stand around 8.1m (26.7ft) tall, with a diameter of 4m (13ft).
The Crew Dragon is equipped with 16 Draco thrusters that are used to maneuver the vehicle in orbit. Each Draco is capable of producing 90 pounds of force in the vacuum of space.
SpaceX engineer John Federspiel, explains: “When we wanted to take Dragon and make it human-rated, I think we took a different approach to spaceship design than has previously been done, because we wanted this to feel like a 21st Century spaceship.

“Probably one of the biggest features of Dragon are the touchscreens on the inside. We designed them not just to be very functional, but with a user experience in mind.”
The three large displays that allow Hurley and Behnken to monitor systems and control the spacecraft are a world away from the analogue buttons, dials and control stick that featured in the cockpit of the shuttle, which flew from 1981 to 2011.
The two Nasa astronauts have been working with SpaceX to get the vehicle ready for its first crewed flight. Hurley admits that the “glass cockpit” took a bit of getting used to.
“As far as actual physical feedback, you certainly don’t get that from the touchscreen,” he says.
“But what you do get is an indication of where you touched and that’s part of the process of flying the vehicle manually is… I touched that button and that made the vehicle go up and I got the return flash that that’s what the vehicle recognised as my input.”
For the types of scenarios where astronauts might need to assume manual control of the normally autonomous craft, such as finishing off a docking sequence with the space station, the touchscreen controls are “much more than adequate”, Hurley adds.
“It just might not be the same thing you’d want to use if you were suited up and trying to fly an entry or descent, for example, like we could do with the space shuttle,” says Behnken.
But tailoring the spacecraft to the user experience involved more than just the design of the controls. “When I think of comfort for the astronauts, it’s really every aspect of how you could interact with the spaceship that comes to mind,” says John Federspiel.

“We have three different seat sizes, we even go so far as moulding the foam around the astronaut’s body so there’s not any pressure points and it’s just generally a pleasurable journey into space.”
But in case anything goes wrong on the pad or during the climb to orbit, SpaceX has designed an innovative abort system for the capsule. The launch escape system (LES) consists of a set of SpaceX-designed SuperDraco engines that fire in the event of an emergency to propel the capsule and its crew safely away from the rocket.
Commenting on the LES, Doug Hurley says: “That perspective for me is huge compared to shuttle, where there were what we call ‘black zones’… scenarios where it didn’t really matter if you had the right combination of failures, you were likely not going to survive.”
In addition, Hurley comments: “The capsule design is a safer design than a winged vehicle under most circumstances.”
Behnken adds: “The space shuttle was 10 times larger in terms of mass than you needed to get into low-Earth orbit… flying on a smaller rocket, really focused on the crew mission… provides another level of safety.”
John Federspiel explains: “Dragon is a spaceship that’s all about safety and reliability. We designed it to be two-fault tolerant, which means that any two things could fail, so I could lose a flight computer and a thruster and I could still bring the crew home safely.”
When it returns to Earth, the Crew Dragon can’t simply land on a runway like the space shuttle. “I think there’s an argument that the return is more dangerous in some ways than the ascent,” says Elon Musk.
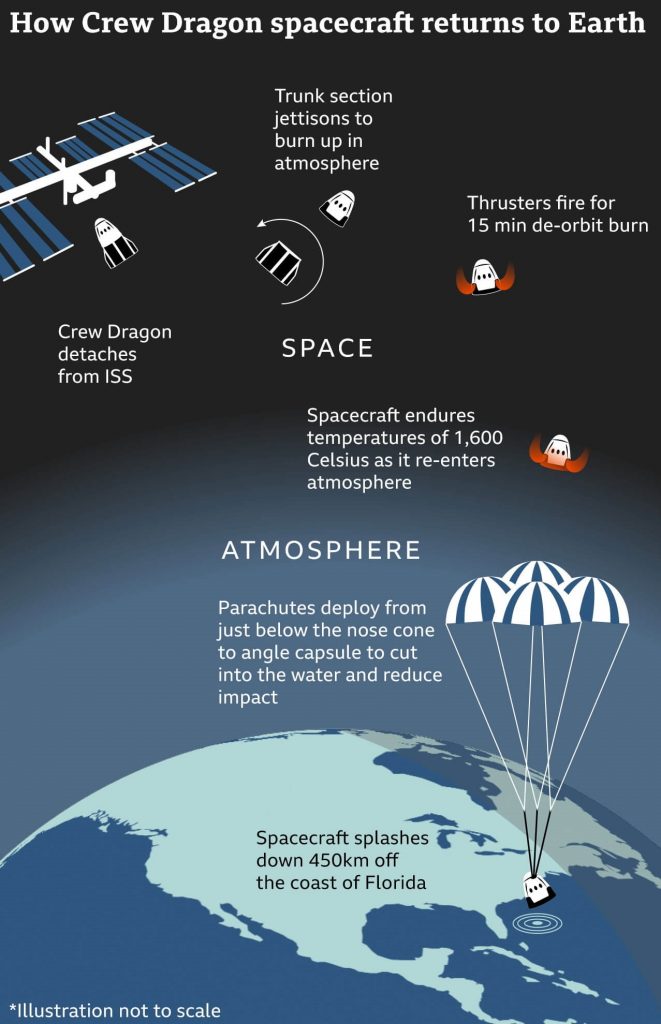
During re-entry, the heat shield must survive temperatures hotter than the surface of the Sun, as the Crew Dragon screams through the atmosphere at up to 25 times the speed of sound.
There’s a minor chance that the spacecraft’s asymmetric design – driven by the placement of its emergency escape system – could cause it to roll too much. Musk has said in the past that the issue, known as roll instability, has been extensively studied, but that it still worries him.
Then, after the fiery re-entry phase, the spacecraft needs to deploy four parachutes to slow its descent.
Finally, the Crew Dragon splashes down in the Atlantic Ocean, 450km off the coast of Florida, where recovery ships will take the astronauts to safety and retrieve the capsule.
Hurley says that while he and Behnken – along with others at Nasa – provided input, “this spacecraft – Crew Dragon – is SpaceX’s design, from start to finish. Make no mistake about that”.
He adds: “Just to see the vehicle come from not very much, a preliminary design, to where it is today, the operability of the vehicle, the clean lines, how it is inside the vehicle, how it is for a crew… we’re just excited to put it through its paces.”