US based GPU manufacturer Nvidia has published a research paper outlining a new artificial intelligence (AI) model capable of converting 2D video clips into detailed 3D models.
The research found that current generative AI models struggle to capture fine details of objects, such as repetitive texture patterns, homogenous colors, and strong color variations. Nvidia’s new AI technology, called Neuralangelo, is said to surpass these problems. Neuralangelo offers high fidelity models and the ability to accurately translate the textures of complex materials from 2D videos.
How might Nvidia AI as a 3D printing tool develop?
Nvidia highlights the potential benefits for creative professionals in particular, who can quickly and easily create virtual objects using footage captured from a smartphone. Art, virtual reality, video game development, robotics, and the production of industrial digital twins have been outlined as potential applications of Neuralangelo.
The company has already demonstrated the wide ranging capabilities of their new AI technology, recreating Michelangelo’s David sculpture and a flatbed truck. Neuralangelo can also reconstruct large scale environments. Nvidia has successfully created a 3D model of the park at their Bay Area campus using birdseye video footage captured by a drone.
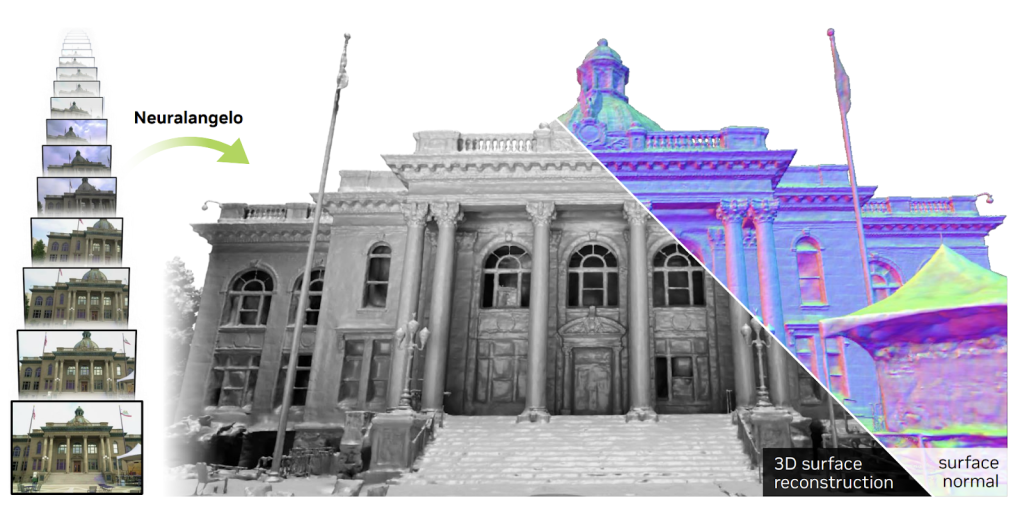

“The 3D reconstruction capabilities Neuralangelo offers will be a high benefit to creators, helping them recreate the real world in the digital world,” commented Ming-Yu Liu, Senior Director of Research at Nvidia, and co-author of the research paper. “This tool will eventually enable developers to import detailed objects – whether small statues or massive buildings – into virtual environments for video games or industrial digital twins.”
While this new AI tool is yet to be combined with 3D printing applications, an Nvidia spokesperson told this could be a future direction. Currently, Neuralangelo’s models cannot be 3D printed.
It’s easy to imagine the potential for additive manufacturing integration with Neuralangelo.
Whether through exporting the AI generated mesh as a printable file in the future, or as part of a digital twin. Presently, digital twins are leveraged for the design and prototyping stages of product development, and further into the product life cycle.
Converting 2D videos into 3D models with AI
Neuralangelo employs Instant Neural Graphics Primitives (NGP) in combination with signal distance functions (SDF) to achieve high quality video conversion. NGP provides hybrid 3D grid structures with a multi resolution hash encoding. This hybrid representation significantly increases the representation power of neural fields, and can capture more fine-grained details.
Effectively, Neuralangelo takes a 2D video of an object or environment, and selects several frames that highlight different viewpoints. Once the camera position of each frame is determined, the AI creates a rough 3D model. This rough rendering is then optimized, sharpening up the details and producing a finished product with high surface quality and accuracy.
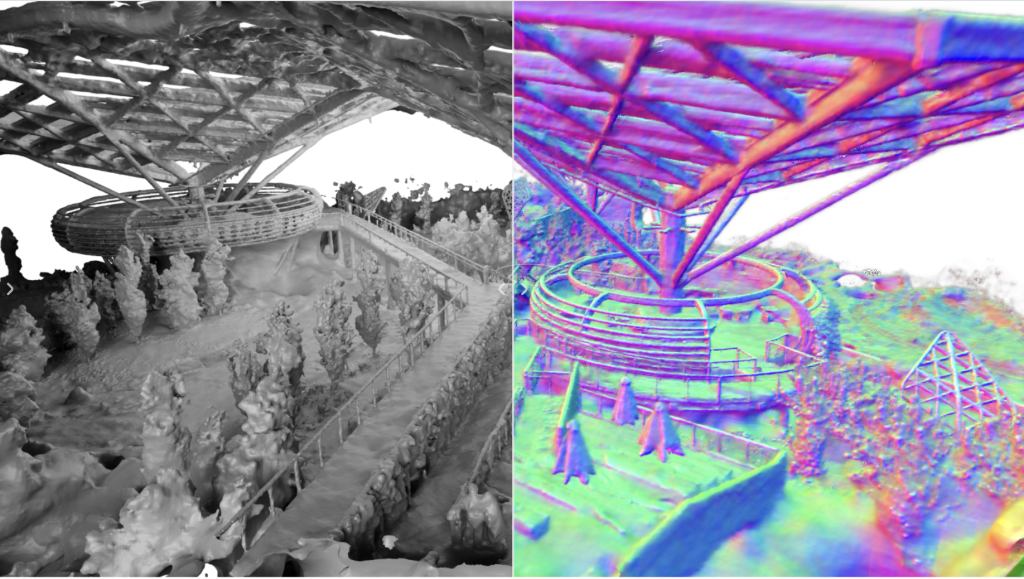
The researchers highlight two factors that are key to this approach. Firstly, using numerical gradients to compute high-order derivatives. This is said to be critical for stabilizing the optimization process. Secondly, a progressive optimization schedule is vital for recovering structures at different levels of detail. This allows for comprehensive and accurate 3D model reconstruction.